

If you agree, we’ll also use cookies to complement your shopping experience across the Amazon stores as described in our Cookie Notice. We also use these cookies to understand how customers use our services (for example, by measuring site visits) so we can make improvements. Typically, reverse osmosis membranes last three years or longer.We use cookies and similar tools that are necessary to enable you to make purchases, to enhance your shopping experiences and to provide our services, as detailed in our Cookie Notice. As long as you get a respectable TDS reading, the membrane does not need to be replaced. What you are measuring is the performance of the reverse osmosis membrane. In other words, if the tap water reads 250, the reverse osmosis water should read around 25 or less. The RO water should be about 1/10 or less the reading of the tap water. Measure the TDS of your tap water, then measure the product water for comparison. When you’re finished, turn the tester off.Hold locks the number on the display so it won’t go away and Temp measures the temperature of the water. The Hold button and the Temp button are features you probably won’t need.The number you see is the TDS (Total Dissolved Solids) of the water expressed in PPM (parts per million).

You’ll ruin the meter if you submerge it too deeply. Insert the tip of the tester (the end where the cover was) into the water to be tested.Remove the cover from the bottom of the tester, then turn on the unit by pressing the On/Off button.If your tap water, for example, has a TDS reading of 250 parts per million, that means that the total content of the minerals dissolved in the water make up 250 parts per million of the total volume.įor practical purposes, TDS measurement is a very effective way to test you reverse osmosis unit’s performance. Dissolved solids in water are mainly its mineral content. It gives a reading in parts per million (ppm) of all the dissolved solids, good or bad. This is a simple but very reliable tester that measures the Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) in water. The noticeable effects when levels exceed that threshold include hardness, colored water, deposits, salty taste, and staining. The EPA has set the maximum contaminant level for TDS in drinking water at 500 parts per million, or 500mg/L. These are contaminants that can cause the water to have an unpleasant look, taste, or smell, but they are not considered a health threat. The EPA has labeled TDS as a secondary contaminant that has an aesthetic effect. The amount and type of solids in your water can affect the hardness and taste. Many are natural and seep into water through the soil, but some come from pipes, sewage, and chemical run-off. The dissolved solids that are typically found in drinking water come from a number of sources. Total dissolved solid levels will vary depending on the type of water being tested, area of the country you are in and source that the water was taken from. Extremely Low Levels of Dissolved Solids: Could be problematic as it can be associated with corrosion and impact pH levels making the water acidic and corrosive.
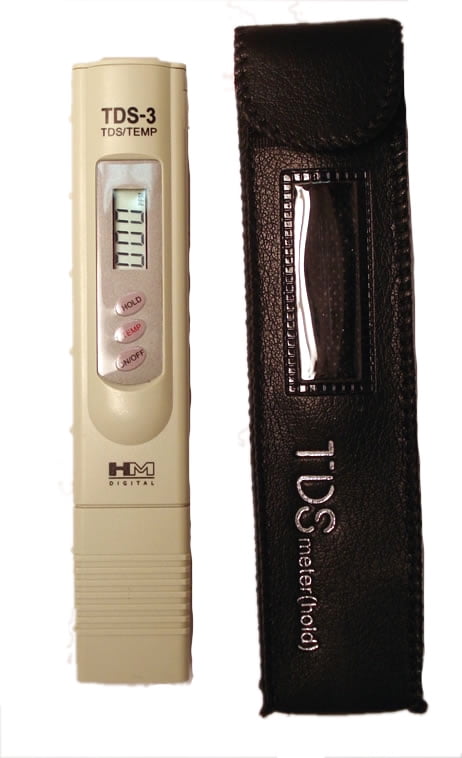

How a TDS Meter Worksīecause the dissolved solids have an electrical charge, the TDS meter can measure the electrical conductivity. TDS testers will not provide you with a reading on what chemicals or contaminants are found in water. Dissolved solids can include minerals, salts, calcium, magnesium, potassium, sodium, bicarbonates, chlorides, sulfates and other organic matter. TDS meter provide you with the tools required to detect the total amount of dissolved solids in water.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
